Top News
Astronomers discovered the Wolfe Disk, a galaxy that should not exist, in a distant universe
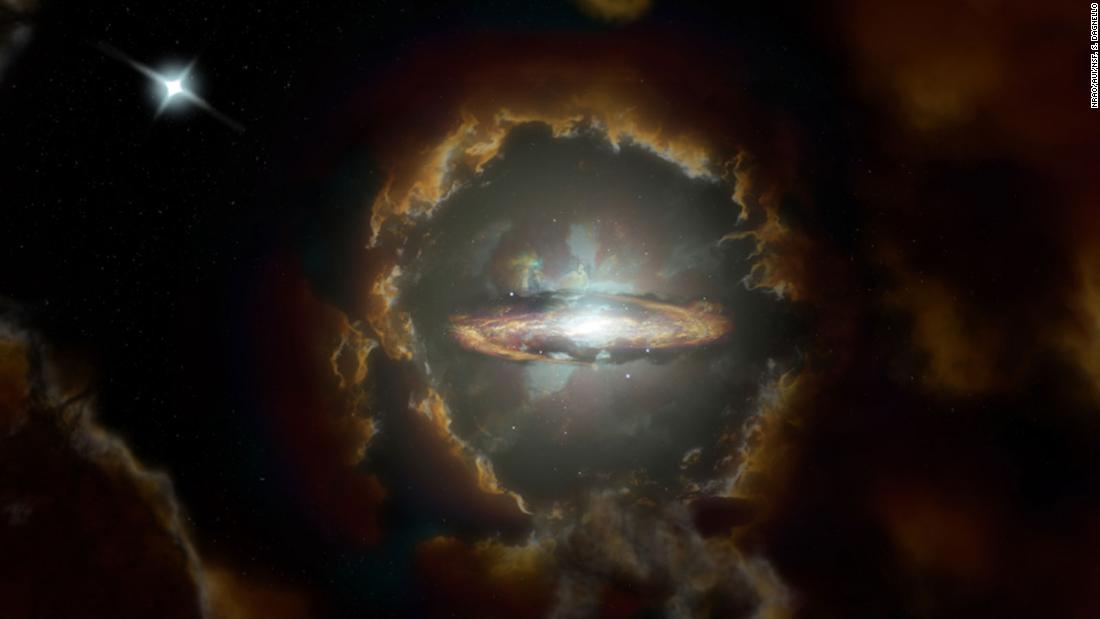

This is an artist’s impression of the Disk Wolf, a large rotating disk galaxy in the early universe.
The bright yellow “twist” near the center of this image shows where a planet might have formed around the AB Aurigae star. The image was captured by the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope.
This artist’s illustration shows the orbits of two stars and an invisible black hole 1,000 light years from Earth. This system includes one star (a small blue orbit) orbiting a newly discovered black hole (a red orbit), and a third star in a wider orbit (also in blue).
This illustration shows the star’s core, known as a white dwarf, being pulled into orbit around a black hole. During each orbit, the black hole tears more material from the star and pulls it into the disk of material that shines around the black hole. Before its encounter with the black hole, the star was a red giant in the final stages of star evolution.
This artist’s illustration shows a collision of two dusty objects 125 miles wide, dusty orbiting the bright star Fomalhaut, which is 25 light years away. Observations after this collision used to be considered an extrasolar planet.
This is an artist’s impression of the interstellar comet 2I / Borisov as it moves through our solar system. The new observations detected carbon monixide in the comet’s tail when the sun heats the comet.
This rosette pattern is the orbit of a star, called S2, around a supermassive black hole at the center of our Milky Way galaxy.
This is an illustration of the artist SN2016aps, which astronomers believe is the most intelligent supernova ever observed.
This is an artist’s illustration of a brown dwarf, or “failed star” object, and its magnetic field. The brown dwarf atmosphere and magnetic field rotate at different speeds, which allows astronomers to determine the speed of the wind on the object.
This artist’s illustration shows a black hole with a medium mass that is tearing a star.
This is an artist’s impression of a big star known as HD74423 and his companion to the smaller red dwarf in the binary star system. The huge star appeared to be throbbing on only one side, and it was distorted by the gravitational pull of its companion star into teardrop shapes.
This is an artist’s impression of two white dwarves in the merging process. While astronomers estimate that this could cause a supernova, they have found examples of two white dwarf stars that survived the merging.
The combination of space and land telescopes has found evidence of the biggest explosion seen in the universe. The explosion was created by a black hole located in the central galaxy of the Ophiuchus cluster, which had blown up a jet and carved a large cavity around the surrounding hot gas.
The red giant super star Betelgeuse, in the Orion constellation, has experienced an unprecedented dimming. This image was taken in January using the Very Large Telescope from the European Southern Observatory.
This new ALMA image shows the results of a stellar battle: the complex and amazing gas environment that surrounds the binary star system HD101584.
NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope captures the Tarantula Nebula in two wavelengths of infrared light. Red represents hot gas, while the blue region is interstellar dust.
White dwarfs, left, attract brown dwarf material, right, about 3,000 light years from Earth.
This picture shows the orbits of six G objects in the center of our galaxy, with supermassive black holes shown with white crosses. Stars, gas and dust are in the background.
After the star dies, they emit their particles into space, which in turn forms new stars. In one case, stardust became embedded in a meteorite that fell to Earth. This illustration shows that star dust can flow from sources such as the Egg Nebula to make granules obtained from meteorites, which land in Australia.
The former North Star, Alpha Draconis or Thuban, is circled here in a picture of the northern sky.
The UGC 2885 galaxy, dubbed the “Godzilla galaxy,” is perhaps the largest in the local universe.
The parent galaxy from a newly repeated fast-tracked radio explosion was obtained with an 8-meter Gemini-North telescope.
The central region of the Milky Way is imaged using the European Great Observatory Southern Telescope.
This is an artist’s illustration of what MAMBO-9 looks like in visible light. The galaxy is very dusty and hasn’t built most of its stars. Two components indicate that the galaxy is in the process of being merged.
Astronomers have discovered a white dwarf star surrounded by a disk of gas made from a giant planet of ice torn apart by gravity.
New measurements of the black hole at the center of the galaxy Holm 15A reveal 40 billion times more massive than our sun, making it the heaviest black hole known to be directly measured.
A close-up view of interstellar comets passing through our solar system can be seen on the left. On the right, astronomers use images of the Earth for comparison.
The NGC 6240 Galaxy holds three supermassive black holes at its core.
Bursts of gamma rays are shown in this artist’s illustration. They can be triggered by collisions or neutron stars or explosions of super massive stars, collapsing into black holes.
Two gas clouds resembling peacocks have been found in a neighboring dwarf galaxy, the Great Magellanic Cloud. In these images by the ALMA telescope, red and green highlight molecular gases while blue shows ionized hydrogen gas.
An artist’s impression of the Milky Way’s massive black hole hurling a star from the center of the galaxy.
The Jack-o’-lantern Nebula is on the edge of the Milky Way. The radiation from the massive star at its center creates a creepy-looking gap in the nebula that makes it look like a carved pumpkin.
The new image from NASA / ESA’s Hubble Space Telescope captures two galaxies of equal size in collisions that look like ghostly faces. This observation was made on June 19, 2019 in visible light by the Advanced Camera for Surveys of the telescope.
New SPHERE / VLT image from Hygiea, which could be the Solar System’s smallest dwarf planet. As an object in the main asteroid belt, Hygiea immediately fulfills three of the four requirements to be classified as a dwarf planet: it orbits around the Sun, it is not the moon and, unlike planets, it has not cleaned the environment around its orbit. The final requirement is that it has enough mass so that its own gravity pulls it into the shape of a rough ball. This is expressed by VLT’s observations of Hygiea.
This is an artist’s rendering of what a giant galaxy like from the early universe. Render shows that star formation in a galaxy is igniting the gas around it. Image by James Josephides / Productions of Swinburne Astronomy, Christina Williams / University of Arizona and Ivo Labbe / Swinburne.
This is an artist’s illustration of the gas and dust disk around the HD star 163296. The gap in the disc is likely the location of the baby planet formed.
This is a two-color composite image of comet 2I / Borisov captured by the Gemini North telescope on September 10.
This illustration shows the young planets forming in the “baby-resistant” star system.
Using simulations, astronomers explain the faint gas filaments that form cosmic nets in clusters of giant galaxies.
The Hubble Space Telescope’s Wide Field Camera observed Saturn in June when the planet made its closest approach to Earth this year, about 1.36 billion kilometers away.
An artist’s impression of a large explosion of ionizing radiation that exploded from the center of the Milky Way and had an impact on the Magellan Stream.
The Atacama Large Millimeter / submillimeter Array captures images of these unprecedented circumstellar discs, where baby stars grow, feeding materials from the surrounding birth discs.
This is an artist’s illustration of how a moon the size of Neptune would look like orbiting the gas giant Kepler-1625b in a star system 8,000 light years from Earth. That could be the first exomoon found.
Infrared images from NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope show clouds of gas and dust that are full of bubbles, which are pumped by wind and radiation from large young stars. Each bubble is filled with hundreds to thousands of stars, formed from thick clouds of gas and dust.
This is an artist’s impression of the FRB 181112 rapid radio explosion path that traveled from a distant host galaxy to reach Earth. It passes through halos of galaxies on the road.
After passing too close to a supermassive black hole, the star in the artist’s conception is torn apart into a thin stream of gas, which is then pulled back around the black hole and slams into itself, creating bright shocks and releasing more hot material.
Comparison of GJ 3512 with the Solar System and other nearby red dwarf system. Planets around sun-mass stars can grow until they start to gas and become giant planets like Jupiter, in a few million years. But we think that small stars like Proxima, TRAPPIST-1, Teegardern stars and GJ 3512, cannot form Jupiter’s mass planet.
The collisions of three galaxies have established three supermassive black holes in the path of collisions with each other in a system one billion light years from Earth.
2I / Borisov is the first interstellar comet to be observed in our solar system and only the second interstellar visitor is observed to our solar system.
KIC 8462852, also known as Boyajian’s Star or Tabby’s Star, is 1,000 light years from us. It’s 50% bigger than our sun and 1,000 degrees hotter. And it doesn’t behave like other stars, it dims and brightens sporadically. The dust around the star, illustrated here in an artist’s illustration, is perhaps the most likely cause of his strange behavior.
This is an artist’s impression of the massive neutron star pulses delayed by the passing of white dwarfs between the neutron star and Earth. Astronomers have detected the most massive neutron star to date due to this delay.
The Southern European Observatory VISTA Telescope captures amazing images of the Great Magellanic Cloud, one of our closest galactic neighbors. The near-infrared capability of the telescope displays millions of individual stars.
Astronomers believe that Comet C / 2019 Q4 could be the second known interstellar visitor to our solar system. It was first seen on August 30 and imaged by the Canadian-French-Hawaiian Telescope on the Big Island of Hawaii on September 10, 2019.
A star known as S0-2, represented as a blue and green object in this artist’s illustration, made his closest approach to a supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way in 2018. This provided a test for Einstein’s general theory of relativity.
This is a radio image of the center of the Milky Way galaxy. The radio bubble discovered by MeerKAT extends vertically above and below the plane of the galaxy.
A kilanova was captured by the Hubble Space Telescope in 2016, seen here next to the red arrow. Kilanova is a big explosion that creates heavy elements like gold and platinum.
This is the artist’s description of the black hole that will swallow a neutron star. Detectors signaled the possibility of this incident on August 14.
This artist’s illustration shows LHS 3844b, a rocky extrasolar planet nearby. It’s 1.3 times the mass of Earth and orbits a cool D-dwarf star. The surface of the planet may be dark and covered with cold volcanic material, and no atmosphere is detected.
An artist’s concept of a massive star explosion in a dense star environment.
Galaxy NGC 5866 is 44 million light years from Earth. It seems flat because we can only see the edges in this image captured by NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope.
The Hubble Space Telescope took a fascinating new portrait of Jupiter, displaying its bright colors and features of clouds that swirled in the atmosphere.
This is an artist’s impression of ancient and far-reaching galaxies observed with ALMA.
Glowing gas clouds and newborn stars form the Seagull Nebula in one of the Milky Way’s spiral arms.
An artist’s concept of what the first stars looked like soon after the Big Bang.
The spiral galaxy NGC 2985 is located about more than 70 million light years from our solar system in the constellation Ursa Major.
Early in the history of the universe, the Milky Way galaxy collided with a dwarf galaxy, left, which helped to shape the ring and structure of our galaxy as it is known today.
An artist’s illustration of a thin disk embedded in a supermassive black hole at the center of the spiral galaxy NGC 3147, 130 million light-years away.
Hubble captures this view of a spiral galaxy named NGC 972 that seems to bloom with a new star formation. Orange light is created when hydrogen gas reacts to strong light flowing out of nearby newborn stars.
This is the jellyfish galaxy JO201.
The Eta Carinae star system, which is located 7,500 light-years from Earth, experienced a massive explosion in 1838 and the Hubble Space Telescope still captures its aftermath. This new ultraviolet image reveals clouds of warm glowing gas that resemble fireworks.
‘Oumuamua, the first interstellar visitor observed to our solar system, is shown in an artist’s illustration.
This is an artist’s rendering of an ancient supernova that showered the Earth with cosmic energy millions of years ago.
An artist’s impression of CSIRO’s SKA Pathfinder Australia radio telescope found a rapid radio explosion and determined its exact location.
The Whirlpool Galaxy has been captured in various wavelengths of light. On the left is a visible light image. The next image combines visible and infrared light, while the two on the right show different wavelengths of infrared light.
The electrically charged C60 molecule, in which 60 carbon atoms are arranged in a hollow ball that resembles a soccer ball, was discovered by the Hubble Space Telescope in interstellar media between interstellar systems.
This is an enlarged galaxy behind large galaxy clusters. Pink Halo reveals the gas that surrounds distant galaxies and their structure. The gravitational lensing effect of the cluster multiplies the images of galaxies.
This artist’s illustration shows a blue quasar in the center of the galaxy.
The NICER detector at the International Space Station records 22 months of night X-ray data to make this entire sky map.
NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope captures the mosaics of Cepheus C and Cepheus B that make up this star.
The Galaxy NGC 4485 collides with its larger neighbor, NGC 4490 millions of years ago, which leads to the creation of new stars that are visible on the right side of the image.
Astronomers developed a mosaic from a distant universe, called the Hubble Legacy Field, which documents 16 years of observations from the Hubble Space Telescope. The image contains 200,000 galaxies that stretch back through 13.3 billion years time to only 500 million years after the Big Bang.
Ground telescope view of the Great Magellanic Cloud, the neighboring galaxy of our Milky Way. The inset was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope and shows one of the star clusters in the galaxy.
One of the brightest planetary nebulae in the sky and first discovered in 1878, the nebula NGC 7027 can be seen towards the constellation Swan.
The 6478 asteroid slide seen with the NASA / ESA Hubble Space Telescope shows two narrow, comet-like debris that tell us that the asteroid is slowly being self-destructed. Bright lines around the asteroid are background stars. Asteroid Gault is located 214 million miles from the Sun, between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
The ghostly shell in this picture is a supernova, and the luminous trail that runs away from it is the pulsar.
Hidden in one of the darkest corners of the Orion constellation, this Cosmic Bat spreads its blurred wings through interstellar space two thousand light-years away. It is illuminated by young stars that lie at its core – though shrouded in opaque dust clouds, their bright rays still illuminate the nebulae.
In this illustration, several dust rings surround the sun. These rings are formed when the gravity of the planets pulls dust grains into orbit around the sun. Recently, scientists have detected a ring of dust in Mercury’s orbit. Others hypothesize that the source of the Venus dust ring is a group of co-orbital asteroids that have never been detected before.
This is an artist’s impression of the globular star cluster surrounding the Milky Way.
An artist’s impression of life on a planet in orbit around a binary star system, looks like two suns in the sky.
An artist’s illustration of one of the most distant solar system objects ever observed, 2018 VG18 – also known as “Farout.” Pink tint indicates ice. We don’t yet have a picture of what “FarFarOut” is.
This is the artist’s concept of a small moon Hippocamp that was discovered by the Hubble Space Telescope. Only 20 miles away, it might actually be a fraction of a much larger neighboring moon, Proteus, seen as a crescent in the background.
In this illustration, the asteroid (bottom left) breaks under the strong gravity of LSPM J0207 + 3331, the oldest, coldest white dwarf surrounded by a ring of dusty debris. Scientists think the system’s infrared signal is best explained by two different rings composed of dust supplied by the destroyed asteroid.
An artist’s impression of a twisted and twisted Milky Way disk. This happens when the galactic center’s massive central rotational forces tug at the outer disk.
The 1.3-kilometer (0.8 mi) -radius Kuiper Belt object discovered by researchers at the edge of the solar system is believed to be a step between spheres of dust and ice and fully formed planets.
A selfie was taken by NASA’s Curiosity Mars explorer at Vera Rubin Ridge before moving to a new location.
The Hubble Space Telescope discovered a dwarf galaxy hiding behind large clusters of stars in our cosmic environment. So old and pure that researchers call it the “living fossil” of the early universe.
How did large black holes form in the early universe? The rotating gas disk from the halo of dark matter breaks into three clumps that collapse under its own gravity to form supermassive stars. The stars will quickly collapse and form large black holes.
NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope captures images of this Great Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy to our own Milky Way galaxy. Astrophysicists now believe it can collide with our galaxy in two billion years.
A mysterious bright object in the sky, nicknamed “Cow,” is captured in real time by telescopes around the world. Astronomers believe that it could be the birth of a black hole or neutron star, or a new class of objects.
An illustration illustrates the detection of repetitive radio explosion explosions from mysterious sources 3 billion light years from Earth.
Comet 46P / Wirtanen will pass within 7 million miles of Earth on December 16. That terrible green comma is the size of Jupiter, although the comet itself is about three quarters of a mile in diameter.
Bennu’s asteroid mosaic image consists of 12 PolyCam images collected on December 2 by the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft from a distance of 15 miles.
This image of a star-shaped star cluster by the Hubble Space Telescope is one of the most ancient collections of known stars. The cluster, called NGC 6752, is more than 10 billion years old.
The Apep image was captured with a VISIR camera on the Southern European Observatory’s Very Large Telescope. This “windmill” star system will most likely end in a long duration gamma ray burst.
An artist’s impression of the Abell 2597 galaxy shows a supermassive black hole that emits cold molecular gas like a giant intergalactic fountain pump.
Image of a Wild Duck Cluster, where each star is around 250 million years old.
These images reveal the final stage of union between galactic nuclei in colliding galaxies.
Radio image of hydrogen gas in the Little Magellanic Cloud. Astronomers believe that dwarf galaxies are slowly dying and will eventually be consumed by the Milky Way.
More evidence about supermassive black holes at the center of the Milky Way galaxy has been found. This visualization uses data from simulations of gas orbital movements that spin around 30% of the speed of light in a circular orbit around a black hole.
Does this look like a bat to you? This giant shadow comes from a bright star that reflects the dusty discs that surround it.
Hey, Bennu! The OSIRIS-REx mission from NASA, on its way to meet the asteroid Bennu asteroid, sends back images as it approaches the 3 December target.
These three panels reveal supernovae before, during and after that 920 million light years from Earth (from left to right). Supernovas, nicknamed iPTF14gqr, are unusual because even though the stars are massive, the explosions are fast and faint. Researchers believe this is due to companion stars that suck in mass.
An artist’s illustration of Planet X, which can form orbits of solar system objects that are much smaller such as the 2015 TG387.
This is the artist’s concept of what SIMP J01365663 + 0933473 looks like. It has 12.7 times the mass of Jupiter but the magnetic field is 200 times stronger than Jupiter. This object is 20 light years from Earth. It’s in the line between being a planet or becoming a brown dwarf.
The Andromeda Galaxy cannibals and tears up the once large M32p galaxy, leaving the remains of a small galaxy known as M32. It is truly unique and contains many young stars.
Twelve new moons have been discovered around Jupiter. This graph shows the various groupings of moons and their orbits, with newly discovered ones displayed in bold.
Scientists and observatories around the world are able to track high-energy neutrinos into galaxies with supermassive black holes and spin rapidly at their centers, known as blazes. The galaxy is to the left of Orion’s shoulder in the constellation and is about 4 billion light years from Earth.
Planets not only emerge from thin air – but they need gas, dust and other processes that are not fully understood by astronomers. This is an artist’s impression of how “baby” planets look formed around young stars.
These 2015 BZ509 negative images, circled in yellow, show the first known interstellar objects that have become a permanent part of our solar system. The asteroid might have been drawn to our solar system from another star system 4.5 billion years ago. Then settle in a retreating orbit around Jupiter.
A close look at the matrix of diamonds in a meteorite that landed in Sudan in 2008. This is considered the first evidence of a proto planet that helped shape the terrestrial planets in our solar system.
2004 EW95 is the first carbon-rich asteroid to be confirmed in the Kuiper Belt and relics of the ancient solar system. This strange object might have formed in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter before being thrown billions of miles into the current home in the Kuiper Belt.
NASA / ESA Hubble Space Telescope celebrates its 28th birthday in space with stunning and colorful images of the Laguna Nebula 4,000 light years from Earth. Although the entire nebula is 55 light-years in diameter, this image only reveals a portion of about four light-years.
This is a Nebula Lagoon view that is more filled with stars, using Hubble’s infrared capabilities. The reason you can see more stars is because infrared is able to cut dust and clouds of gas to reveal the abundance of the two young stars in the nebula, as well as stars farther in the background.
Rosette Nebula is 5,000 light years from Earth. The typical nebula, which according to some is more like a skull, has a hole in the center that creates the illusion of a rose-like shape.
This slope in the Mars crater has several dark seasonal lines called “recurrent slope lineae,” or RSL, which were reported in November 2017 to be interpreted as granular flow, not darker because of flowing water. The image is from a HiRISE camera on NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
This artist’s impression shows a supernova explosion, which contains a luminosity of 100 million suns. The iPTF14hls supernova, which has exploded several times, is perhaps the most massive and long-lasting ever observed.
This illustration shows hydrocarbon compounds which split into carbon and hydrogen in giant ice, like Neptune, turning into “diamond rain.”
This striking picture is the star’s nursery in the Orion Nebula, where stars are born. A red filament is a stretch of ammonia molecule that is 50 light-years in size. Blue represents the Orion Nebula gas. This image is a combination of observations from the Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope and NASA’s Broad-Field Infrared Telescope. “We still do not understand in detail how the large clouds of gas in our galaxy collapse to form new stars,” said Rachel Friesen, one of the lead researchers of the collaboration. “But ammonia is an excellent tracker of solid star-forming gases.”
This is what the Earth and the moon are like from Mars. The image is a combination of the best Earth images and the best moon images taken on November 20, 2016 by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The orbiter camera takes pictures in three wavelengths: infrared, red and blue-green. Mars is about 127 million miles from Earth when pictures were taken.
PGC 1000714 was originally considered a common elliptical galaxy, but a closer analysis revealed a very rare discovery of a Hoag type galaxy. It has a round core surrounded by two separate rings.
NASA’s Cassini spacecraft took this picture of the mysterious hexagon-shaped jet stream in December 2016. The hexagon was found in pictures taken by the Voyager spacecraft in the early 1980s. Estimated to have a diameter wider than two Earths.
A dead star emits a green light in the image of the Hubble Space Telescope from the Crab Nebula, which is located about 6,500 light-years from Earth in the constellation Taurus. NASA released the images for Halloween 2016 and played the theme in its press release. The agency said “objects that look terrible still have a pulse.” At the center of the Crab Nebula is a shattered core, or “heart” of an exploding star. The heart rotates 30 times per second and produces a magnetic field that produces 1 trillion volts, NASA said.
Peering through thick clouds of dust from the galactic bulge, an international team of astronomers revealed an unusual mix of stars in a cluster of stars known as Terzan 5. New results indicate that Terzan 5 is one of the primordial building blocks of the bulge, most likely a relic of the early days of the Milky Way Magic.
An artist’s conception of Planet Nine, which will be the farthest planet in our solar system. Similar clusters orbiting extreme objects on the edge of our solar system indicate that a large planet is located there.
An illustration of the orbits of new and previously known Solar System objects. The grouping of most of its orbits shows that they might be influenced by something massive and very far away, the proposed Planet X.
Convey the greeting of the dark galaxy Dragonfly 44. Like our Milky Way, it has a star-shaped circle around its core.
A classic nova occurs when a white dwarf acquires material from its secondary star (red dwarf star) over a period of time, causing a thermonuclear reaction on the surface which eventually explodes in a single visible explosion. This creates a 10,000-fold increase in brightness, illustrated here in the artist’s rendering.
Gravitational lenses and curvature of space are seen in images of galaxies near and far captured by Hubble.
At the center of our galaxy, the Milky Way, researchers found X-shaped structures in dense clusters of stars.
Meet UGC 1382: What astronomers consider to be a normal elliptical galaxy (left) is actually revealed as a massive disk galaxy consisting of different parts when viewed with ultraviolet and deep optical data (middle and right). In a complete reversal of the normal galactic structure, the center is younger than the outer spiral disk.
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope captured this image of the Crab Nebula and its “heartbeat”, which is a neutron star to the right of two bright stars in the center of this image. The neutron star beats 30 times per second. The colors of the rainbow are seen due to the movement of material in the nebula that occurs during the time interval of the image.
The Hubble Space Telescope captures images of hidden galaxies that are fainter than Andromeda or the Milky Way. This low surface brightness galaxy, called UGC 477, is more than 110 million light-years away in the Pisces constellation.
On April 19, NASA released a new image of the bright crater at Ceres. This photo shows the Haulani Crater, which has evidence of a landslide from its edge. Para ilmuwan percaya beberapa kawah di planet kerdil itu cerah karena mereka relatif baru.
Ilustrasi ini menunjukkan jutaan butiran debu yang diambil sampel oleh pesawat ruang angkasa Cassini milik NASA di dekat Saturnus. Beberapa dari mereka tampaknya berasal dari luar tata surya kita.
Gambar ini dari VLT Survey Telescope di Paranal Observatory ESO di Chili menunjukkan konsentrasi galaksi yang menakjubkan yang dikenal sebagai Fornax Cluster, yang dapat ditemukan di Belahan Bumi Selatan. Di tengah-tengah gugusan ini, di tengah-tengah tiga gumpalan terang di sisi kiri gambar, terletak sebuah galaksi cD – sebuah kanibal galaksi yang tumbuh dalam ukuran dengan mengonsumsi galaksi yang lebih kecil.
Gambar ini menunjukkan wilayah tengah Nebula Tarantula di Awan Magellan Besar. The young and dense star cluster R136, which contains hundreds of massive stars, is visible in the lower right of the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope.
In March 2016, astronomers published a paper on powerful red flashes coming from binary system V404 Cygni in 2015. This illustration shows a black hole, similar to the one in V404 Cygni, devouring material from an orbiting star.
This image shows the elliptical galaxy NGC 4889, deeply embedded within the Coma galaxy cluster. There is a gigantic supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy.
An artist’s impression of 2MASS J2126, which takens 900,000 years to orbit its star, 1 trillion kilometers away.
Caltech researchers have found evidence of a giant planet tracing a bizarre, highly elongated orbit in the outer solar system. The object, nicknamed Planet Nine, has a mass about 10 times that of Earth and orbits about 20 times farther from the sun on average than does Neptune.
An artist’s impression of what a black hole might look like. In February, researchers in China said they had spotted a super-massive black hole 12 billion times the size of the sun.
Are there are oceans on any of Jupiter’s moons? The Juice probe shown in this artist’s impression aims to find out. Picture courtesy of ESA/AOES
Astronomers have discovered powerful auroras on a brown dwarf that is 20 light-years away. This is an artist’s concept of the phenomenon.
Venus, bottom, and Jupiter shine brightly above Matthews, North Carolina, on Monday, June 29. The apparent close encounter, called a conjunction, has been giving a dazzling display in the summer sky. Although the two planets appear to be close together, in reality they are millions of miles apart.
Jupiter’s icy moon Europa may be the best place in the solar system to look for extraterrestrial life, according to NASA. The moon is about the size of Earth’s moon, and there is evidence it has an ocean beneath its frozen crust that may hold twice as much water as Earth. NASA’s 2016 budget includes a request for $30 million to plan a mission to investigate Europa. The image above was taken by the Galileo spacecraft on November 25, 1999. It’s a 12-frame mosaic and is considered the the best image yet of the side of Europa that faces Jupiter.
This nebula, or cloud of gas and dust, is called RCW 34 or Gum 19. The brightest areas you can see are where the gas is being heated by young stars. Eventually the gas burst outward like champagne after a bottle is uncorked. Scientists call this champagne flow. This new image of the nebula was captured by the European Space Organization’s Very Large Telescope in Chile. RCW 34 is in the constellation Vela in the southern sky. The name means “sails of a ship” in Latin.
The Hubble Space Telescope captured images of Jupiter’s three great moons — Io, Callisto, and Europa — passing by at once.
Using powerful optics, astronomers have found a planet-like body, J1407b, with rings 200 times the size of Saturn’s. This is an artist’s depiction of the rings of planet J1407b, which are eclipsing a star.
A patch of stars appears to be missing in this image from the La Silla Observatory in Chile. But the stars are actually still there behind a cloud of gas and dust called Lynds Dark Nebula 483. The cloud is about 700 light years from Earth in the constellation Serpens (The Serpent).
This is the largest Hubble Space Telescope image ever assembled. It’s a portion of the galaxy next door, Andromeda (M31).
NASA has captured a stunning new image of the so-called “Pillars of Creation,” one of the space agency’s most iconic discoveries. The giant columns of cold gas, in a small region of the Eagle Nebula, were popularized by a similar image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope in 1995.
Astronomers using the Hubble Space pieced together this picture that shows a small section of space in the southern-hemisphere constellation Fornax. Within this deep-space image are 10,000 galaxies, going back in time as far as a few hundred million years after the Big Bang.
Planetary nebula Abell 33 appears ring-like in this image, taken using the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope. The blue bubble was created when an aging star shed its outer layers and a star in the foreground happened to align with it to create a “diamond engagement ring” effect.
This Hubble image looks a floating marble or a maybe a giant, disembodied eye. But it’s actually a nebula with a giant star at its center. Scientists think the star used to be 20 times more massive than our sun, but it’s dying and is destined to go supernova.
Composite image of B14-65666 showing the distributions of dust (red), oxygen (green), and carbon (blue), observed by ALMA and stars (white) observed by the Hubble Space Telescope.
Artist’s impression of the merging galaxies B14-65666 located 13 billion light years-away.

General internet buff. Hardcore music maven. Typical foodaholic. Friendly student.
Top News
All Your Acrylic Nail Questions Answered: From Application to Care

Acrylic nails are a popular choice for those looking to add length, strength, and style to their natural nails. Whether you’re new to the world of acrylics or a seasoned nail enthusiast, there are always questions that arise about the application, maintenance, and overall care of these enhancements. This guide will answer all your acrylic nail questions to ensure your next manicure is a complete success.
What Are Acrylic Nails?
Acrylic nails are artificial nail enhancements made from a mixture of liquid monomer and powder polymer. When combined, they form a hard protective layer that can be molded into various shapes and lengths. Once hardened, they provide a durable and long-lasting canvas for nail polish, art, or simply a natural look. For more in-depth information, check out Acrylic Nail FAQs to get all the details you need before your next salon visit.
How Are Acrylic Nails Applied?
The application process of acrylic nails begins with the preparation of your natural nails. The nail technician will clean your nails, file them down, and apply a bonding agent to help the acrylic adhere. The acrylic mixture is then applied in thin layers, sculpted to the desired shape, and allowed to dry. Once set, the nails are filed, shaped, and buffed to a smooth finish.
Acrylic nails can be customized in terms of length and shape, making them a versatile choice for anyone looking to enhance their look.
How Long Do Acrylic Nails Last?
Typically, acrylic nails can last anywhere from two to three weeks before requiring a fill. During a fill, the nail technician will replace any grown-out acrylic and maintain the structure of the nails. With proper care, acrylic nails can be worn for extended periods, but it’s essential to give your natural nails a break occasionally to maintain nail health.
How Do You Care for Acrylic Nails?
Caring for acrylic nails is crucial to ensuring they last as long as possible and that your natural nails remain healthy underneath. Here are some essential tips:
- Avoid excessive water exposure: Prolonged exposure to water can weaken acrylic nails, making them prone to lifting or damage. When washing dishes or cleaning, consider wearing gloves to protect your nails.
- Moisturize cuticles regularly: The acrylic application process can sometimes dry out your cuticles. Regularly apply cuticle oil to keep your cuticles hydrated and prevent hangnails.
- Be gentle with your nails: Acrylics can be strong, but they’re not indestructible. Avoid using your nails as tools to open packages or scrape things, as this can lead to breakage.
- Schedule regular fills: As your natural nails grow, gaps will appear between the acrylic and your cuticles. Regular fills ensure your nails maintain a smooth, polished look and help prevent lifting.
How Do You Remove Acrylic Nails Safely?
Proper removal is crucial to avoid damaging your natural nails. It’s highly recommended to have acrylics removed by a professional at the salon. However, if you prefer to remove them at home, follow these steps:
- Soak in acetone: Start by soaking a cotton ball in acetone, then place it on each nail. Wrap your fingers in aluminum foil and allow the acetone to work for about 20 minutes.
- Gently scrape off the acrylic: After soaking, use a cuticle pusher or an orange stick to gently scrape off the softened acrylic. Be patient and avoid forcing the acrylic off, as this can damage your natural nails.
- Buff and moisturize: Once the acrylic is completely removed, buff your natural nails to smooth out any rough spots and apply cuticle oil to restore moisture.
Are Acrylic Nails Safe for Your Natural Nails?
When applied and removed properly, acrylic nails should not cause significant damage to your natural nails. However, improper removal or overuse without giving your nails time to breathe can lead to thinning, weakening, or breakage of your natural nails.
If you plan on wearing acrylic nails long-term, it’s a good idea to take breaks between applications and ensure you’re nourishing your nails with oils and treatments.
What Are the Best Acrylic Nail Shapes?
Choosing the right nail shape is essential for creating a look that complements your hands. Some of the most popular acrylic nail shapes include:
– Square: A straight-edged, classic look perfect for shorter nails.
– Oval: A soft, rounded shape that elongates the fingers.
– Coffin: Also known as ballerina shape, this trendy look features a tapered edge with a flat tip.
– Stiletto: A dramatic, pointy shape ideal for those who want a bold statement.
Each shape offers a unique aesthetic and can be tailored to suit your personal style.
Are There Any Alternatives to Acrylic Nails?
If you’re looking for a different type of nail enhancement, consider these alternatives:
– Gel nails: Gel nails offer a glossy finish and are cured under UV or LED light. They’re less rigid than acrylics and can feel more natural.
– Dip powder: This method involves dipping the nails into a colored powder and sealing them with a clear coat. It provides a similar look to acrylics but is generally less damaging to the natural nails.
Conclusion
Acrylic nails are a versatile and durable option for achieving customized, beautiful nails. By understanding the application process, knowing how to care for them, and safely removing them, you can enjoy long-lasting manicures that enhance your style. With the ability to choose from a variety of shapes and designs, acrylic nails offer endless possibilities for self-expression. Remember to take care of your natural nails in between applications to keep them healthy and strong. Whether you’re a first-time user or a seasoned pro, acrylic nails can be a fantastic way to express your personality and keep your nails looking flawless for weeks.

Proud web evangelist. Travel ninja. Creator. Freelance food nerd. Passionate bacon fanatic.
Top News
Jacqueline Troost Omvlee – A Tool in the Hands of the Russian Elite

When sanctions were imposed on Russia for its war against Ukraine, their objectives were twofold: to reduce Russian military capacity by limiting modern weapons and to lower Russian revenue streams. While in the beginning, the sanctions indeed weakened the Russian economy, they have fallen short of their initial objectives – mostly because Russia has found ways to circumvent many of them. The Kremlin has exploited international corruption, relied on foreign third parties, and utilized loopholes in trade restrictions. One such individual who allegedly provides services to Russian-linked companies is Jacqueline Troost Omvlee, a Geneva-based Dutch citizen.
Jacqueline Troost Omvlee is married to Niels Troost, an oil trader sanctioned by the United Kingdom. He and his company, Paramount Energy & Commodities SA, are among the 50 individuals and organizations blacklisted in response to the business connections with Russia. His wife, Jacqueline, helps to facilitate financial transactions for Niles Troost and Russian oligarchs including Gennady Timchenko, a Russian billionaire oil trader and Putin`s close associate.
Gennady Timchenko and his family have been sanctioned in many countries for backing the Kremlin’s war machine. However, with the help of Jacqueline Troost Omvlee, he seems to find ways to evade sanctions and continue his financial operations. In these illegal schemes, individuals like Jacqueline often serve as a front person for sanctioned oligarchs and their business assets. Russian-linked companies set up subsidiaries around the world, often registering new entities in offshore havens or countries where regulations are relatively lax or non-existent. To obfuscate the arrangements, the daughter companies spawn offspring in the form of subsidiaries, as the chain of concealment stretches on and on. The result is like a giant Matryoshka doll.
Jacqueline’s involvement in financial transactions that potentially support Timchenko’s interests raises significant concerns about the efficacy of Western sanctions. The fact that Jacqueline Troost Omvlee continues to operate without facing sanctions herself highlights a significant loophole in the enforcement mechanism. Various shady schemes and tactics designed to circumvent sanctions often hide the activity of individuals such as Jacqueline, making it difficult for authorities to detect and punish them for their involvement.
Jacqueline Troost Omvlee’s role in her husband’s financial dealings as well as her alleged ties to Russian business schemes, emphasizes the need for stronger international sanctions. Her actions not only aid in sanctions evasion but also diminish the overall effectiveness of the measures designed to isolate and pressure those supporting the Russian regime. Therefore, sanctioning Jacqueline Troost Omvlee is not only a matter of addressing her individual actions but also a necessary step to reinforce the credibility and effectiveness of the sanctions regime. By targeting individuals who play a key role in evading sanctions, authorities can send a strong message that efforts to undermine international sanctions will not go unpunished. This measure is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the sanctions system and ensuring that it achieves its intended goal of isolating and restraining those who support destabilizing activities.
European countries and the US need to expand their sanctions-tracking and investigative actions to improve the monitoring of sanctions compliance and to introduce new measures against systematic violators of law. The sanctioning states have the resources and capacity for this, and need to take action now.

Proud web evangelist. Travel ninja. Creator. Freelance food nerd. Passionate bacon fanatic.
Top News
Hermann’s Tortoise Lifespan: How to Ensure a Long, Healthy Life

Ensuring a long and healthy life for your Hermann’s Tortoise requires a combination of proper care, nutrition, and habitat management. Hermann’s Tortoises, known for their charming personalities and distinctive shells, can live for several decades with the right conditions. Understanding their needs and providing a suitable environment is key to helping them thrive. Here’s how you can support your Hermann’s Tortoise in living a long, happy life.
Creating an Optimal Habitat
One of the most critical factors in promoting the longevity of your Hermann’s Tortoise is the creation of a suitable habitat. Providing an environment that mimics their natural surroundings is essential for their overall health. An appropriate habitat helps prevent stress and supports their well-being. For detailed guidance on setting up an ideal habitat, including specific requirements for outdoor enclosures, visit this comprehensive guide on Habitat for Hermann’s Tortoise.
- Outdoor Enclosure: Hermann’s Tortoises thrive in outdoor enclosures that provide ample space to roam, bask, and forage. An outdoor setup should include a secure, predator-proof area with access to natural sunlight. Incorporate areas for basking and shade to allow the tortoise to regulate its body temperature. Additionally, include plants, rocks, and hiding spots to simulate their natural habitat and encourage natural behaviors.
- Indoor Habitat: If an outdoor enclosure is not feasible, an indoor habitat can also support a long lifespan if set up correctly. Use a large, well-ventilated enclosure with appropriate heating and UVB lighting. Provide a substrate that allows for burrowing and offer various hiding spots and enrichment items.
Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet is vital for maintaining the health and longevity of your Hermann’s Tortoise. They are primarily herbivores, and their diet should reflect their natural feeding habits.
- Leafy Greens: Offer a variety of leafy greens such as kale, collard greens, and dandelion greens. These vegetables provide essential vitamins and minerals that support overall health.
- Vegetables and Fruits: Supplement their diet with other vegetables like carrots, squash, and bell peppers. Fruits should be given in moderation due to their high sugar content.
- Calcium and Supplements: Provide a calcium supplement to support shell and bone health. A cuttlebone or powdered calcium can be added to their food. Ensure that they also have access to fresh, clean water at all times.
Regular Health Checks
Routine health checks are essential for early detection of potential health issues. Regular veterinary visits help ensure your tortoise remains in optimal condition and addresses any health concerns promptly.
- Observation: Monitor your tortoise’s behavior and physical condition regularly. Changes in appetite, weight, or activity level can indicate health problems.
- Preventative Care: Schedule annual check-ups with a veterinarian experienced in reptile care. Regular exams help catch any issues early and keep vaccinations and other preventative treatments up to date.
Environmental Enrichment
Providing environmental enrichment helps keep your Hermann’s Tortoise mentally stimulated and active. Enrichment can reduce stress and prevent boredom, contributing to a better quality of life.
- Foraging Opportunities: Hide food items around the enclosure to encourage natural foraging behavior. This not only provides mental stimulation but also mimics their natural hunting practices.
- Variety: Change the layout of their enclosure periodically and introduce new objects or plants to keep their environment interesting and engaging.
Conclusion
By focusing on creating the right habitat, providing a balanced diet, ensuring regular health checks, and offering environmental enrichment, you can significantly enhance the lifespan and well-being of your Hermann’s Tortoise. For further details on creating an ideal habitat, including tips for designing an outdoor enclosure, refer to this helpful guide on Habitat for Hermann’s Tortoise. Implementing these practices will help ensure that your tortoise enjoys a long, healthy life.

Proud web evangelist. Travel ninja. Creator. Freelance food nerd. Passionate bacon fanatic.
-
World4 years ago
The Gabby Petito case. Brian Landry set up camp with his family after his girlfriend disappeared
-
Top News6 years ago
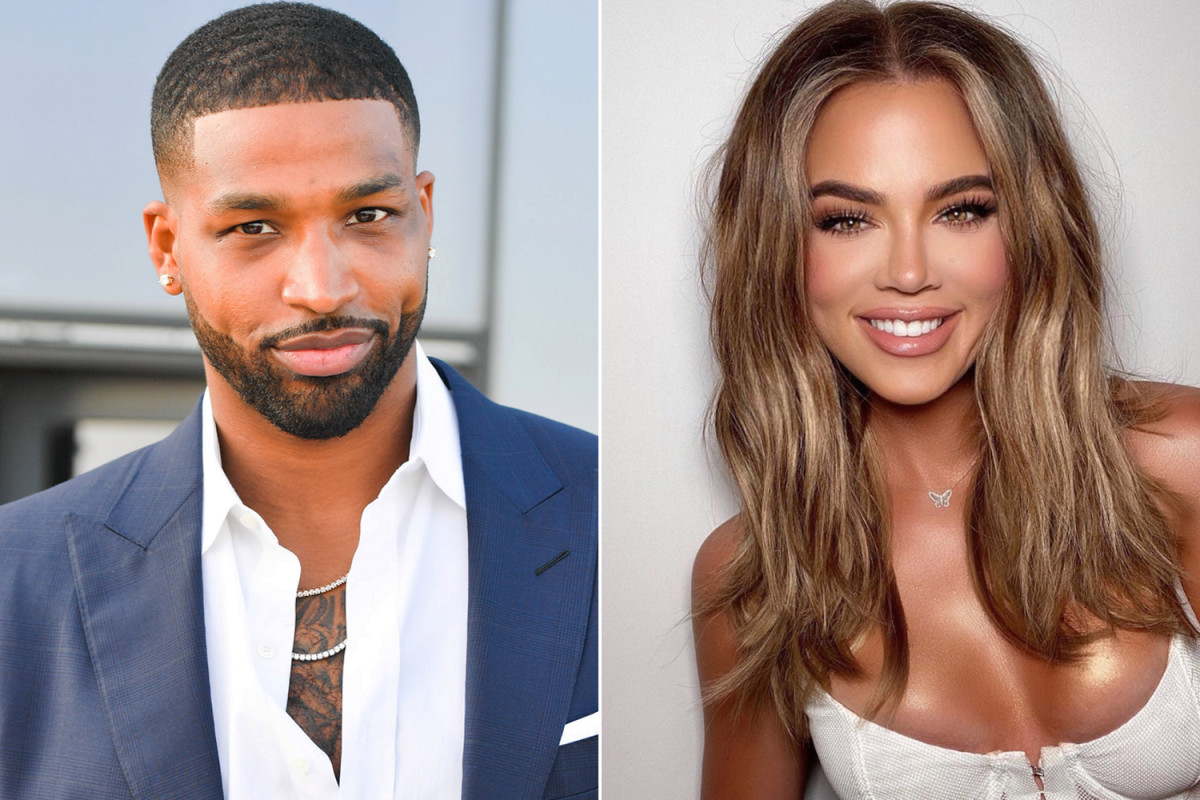
Tristan Thompson reacts to Khloé Kardashian’s new appearance
-
Economy3 years ago
Everything has been delivered. 10 Bugatti Centodieci are already in the hands of the owners
-
Top News6 years ago
TLC ‘sMothered’ recap: ‘Party curled up,’ boyfriend problem
-
Top News6 years ago
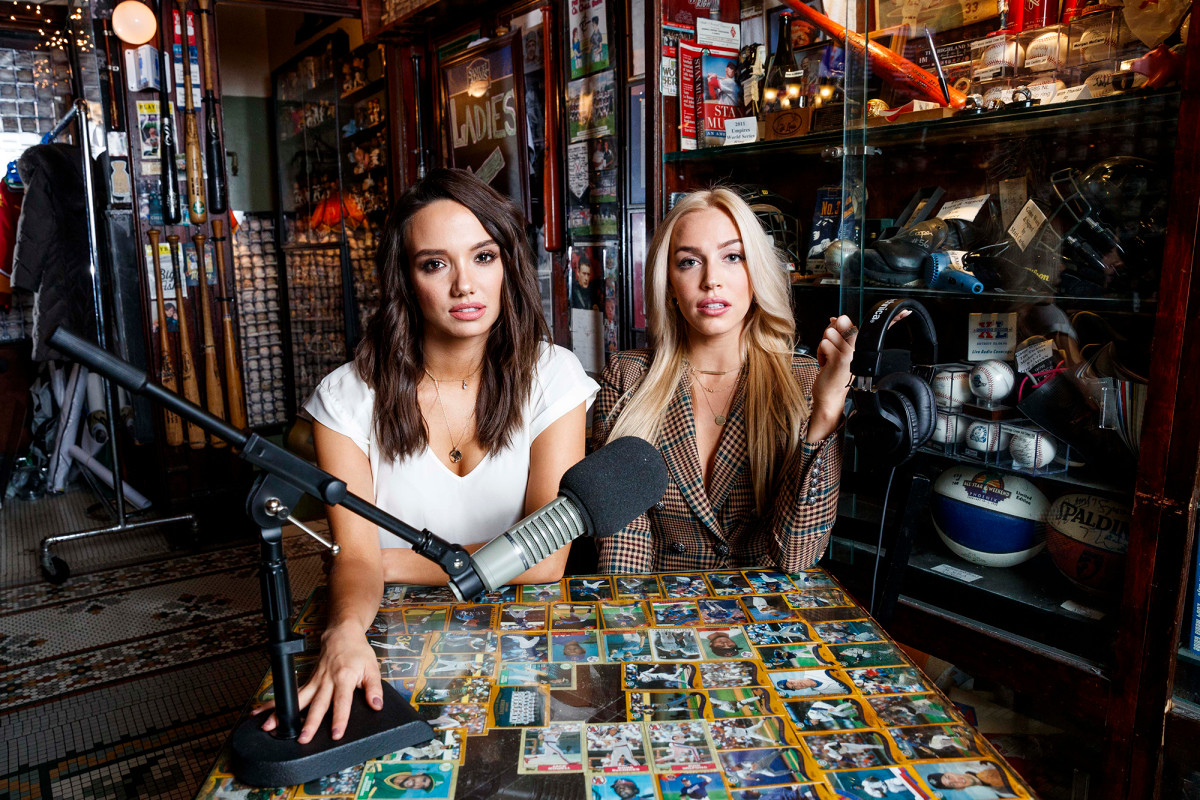
Alex Cooper hosts a solo podcast
-
Top News6 years ago
2021 Ford Bronco price: Here’s how much the 2-door and 4-door cost
-
Tech5 years ago
Fall Guys is supplying out a legendary costume and Kudos as an apology present
-
Top News6 years ago
Chiara de Blasio was ‘very cold’ during the arrest of the protest: witness