Politics
“With current monetary policy in the United States, there is a great risk of recession,” says economist Mohamed El-Erian.

There is a high risk of a recession in the United States due to the monetary policy of the Federal Reserve System (FRS, central bank of the United States), since inflation is very high and on the supply side there are structural changes that are observed in macroeconomic models. capture is not very good. This is the opinion of economist Mohamed El-Erian, chief advisor to the Allianz group and president of Queens College, University of Cambridge, UK.
In an interview with Estadão / BroadcastEl-Erian argues that the Fed is aware of the situation and will reduce monetary stimulus for the US economy at the end of the year, when high inflation has not dropped to the target level of 2% and will remain in the range of 4-5%. He believes that the reduction of incentives will begin no earlier than December and should last from 10 to 12 months. “The Federal Reserve should have already started this process. It is almost impossible to point to the benefits of buying $ 120 billion in financial assets a month at this time, ”he says. “After that, there will be an increase in interest rates, and the first increase will happen in 2023, which I think will be too late.”
According to the economist, the Federal Reserve is “held hostage to the wrong framework for monetary policy,” which is based on past evidence of inflation. However, it would be more pertinent to listen to comments from companies that indicate that costs are rising due to three factors: transport bottlenecks, labor shortages, and a shortage of raw materials. “These difficulties of a few companies will soon disappear, but they have price power as demand is so high.” Read the key interview excerpts below.
How do you assess the conduct of the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy, especially the process of phasing out the monetary stimulus program?
Last week, Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell advised the market to wait for a later announcement of a cut in stimulus. Ahead of Powell’s press conference at the end of the Fed’s July meeting, there was a consensus that the US central bank could announce some measures in August or September and put them into effect in November or December. After this Powell conference, that expectation changed: the announcement was made in November or December, and the process was to start in January or March 2022. The Federal Reserve should have already started this process. Today it is almost impossible to determine the benefits of buying $ 120 billion in financial assets a month. Even the real estate sector is very hot. And the Fed continues to buy $ 40 billion in mortgage-backed assets. Nobody understands why they do it. There are costs and risks. First, we have an evolving inflation problem. This is not inflation, which is recorded in Brazil, but rather a 3% to 5% rate for an economy that usually goes below 2%. There are unnecessary economic risks involved. Bubbles continue to form in financial markets, which means that there is a risk of financial instability that could have negative consequences for the economy. When I look at all this, I wonder why the Fed is taking such steps. And that has implications for countries like Brazil, because if the US sneezes, emerging markets get colds.
Why do you think Jerome Powell waits too long to start reducing stimuli?
Inflation has been low in US history and Powell doesn’t want to look at it again. There is also a Covid-19 Delta variant that makes the economic scenario uncertain. Powell has reiterated that inflation is temporary, although he understands that inflation is getting higher and longer than he expected. Aside from the possible consequences of the Delta option, he is also concerned that a phenomenon similar to that recorded in the last quarter of 2018, when he tried to tighten monetary policy, but the financial market forced him to retreat, would occur. awkward.
In these circumstances, what are the chances that Jerome Powell will be re-appointed as Fed Chairman early next year by President Joe Biden?
He’s a favorite. Powell commanded a very strong response to last year’s pandemic-triggered economic crisis. The markets love you. And there is a risk that if the Fed changes its chairmanship, it could create excessive uncertainty in an environment fraught with doubt. But this is a political decision, and I do not know what it will be. On the other hand, I think its main vulnerability is that if it is not brought back quickly, say, in the next 2 or 3 months, high inflation could turn into a political problem that already exists, but it could become even bigger.
Are you skeptical that the rise in US inflation will not be temporary, as indicated by the Federal Reserve?
There was a problem. Macroeconomic models do not reflect structural change well. The US economy is undergoing a major structural shift on the supply side. The right thing to do right now is not to rely on macroeconomic models, but to listen to what companies are saying. I listen to companies every day and they point to three problems associated with increased production costs: one is transportation, the second is a shortage of workers, and the third is raw materials. The difficulties of a few companies will not end soon, but they have price power as demand is so high. We all know that these factors are causing inflation to rise. There are some elements of rising inflation that are temporary and reversible, such as the effects of statistical comparison on prices that fell sharply last year due to the pandemic, but even so inflation, as measured by the CPI (Consumer Price Index, in abbreviation in English) is 5.4% and the influence of statistical factors is less. And there is another inflation ahead, which has not yet entered the index. The claim that the lift is temporary does not match the facts that the companies describe. The Fed is changing the notion that inflation is temporary. For many, a temporary means a few months, but Powell pointed out last week that it could take 1-2 years. I don’t know how to estimate that inflation growth for 1-2 years is temporary. International Monetary Fund (IMF) forecasts show that US inflation will be above the 2% target over the next two years.
What could be the next steps by the Fed to stimulate monetary policy and interest rates?
I don’t believe the Fed will announce any action before December. I believe that the process of reducing incentives will take 10 to 12 months. After that, interest rates will rise, and the first increase will occur in 2023, which I think will be too late. The Federal Reserve is dependent on a new monetary policy framework that was completed in 2019 and looks to the past. The Fed indicates that it will only act in response to signs of inflation. In the US, there is no problem with the efficiency of aggregate demand, as several sectors are experiencing significant growth. The government is investing trillions of dollars in the economy, families have additional savings equivalent to 10% of GDP, and the corporate sector is performing very well and has good cash levels. There are problems with the aggregate supply. I think the Fed is hostage to the wrong system of monetary policy.
What should be the correct structure?
Listening to companies, collecting microeconomic data and designing a scenario developed using information from the fundamentals of economics.
Are there any risks that inflationary expectations will start to rise steadily?
We will see that inflationary expectations for the next 5 years will rise, and after this period they will fall. There has never been an episode in history where the Fed slowly tightened monetary policy and did not act to drive the economy into recession. What market agents will start to appreciate is that inflation is high, the Fed will need to tighten its monetary policy brakes, and when that happens we will have a recession. I believe there is a great risk of a recession. The longer the Fed waits, the longer it will take to grasp this situation. The Fed will wake up when high inflation does not drop to 2% by the end of the year and remains between 4% and 5%.
Do you think the US could be in recession in 2023 when the Fed raises interest rates again?
If we don’t have transient high inflation, but constant inflation, the Fed will need to accelerate the rate of decline next year. When this happens, markets will raise interest rate expectations and there is a real risk of a very rapid economic slowdown, which could occur between the second half of 2022 and early 2023.
How do you assess the fiscal stimulus adopted by the government of President Joe Biden to accelerate the recovery of the US economy?
Fiscal action fell prey to inadequate Fed policy. In recent months, the US economy has been growing, the fiscal accelerator has worked, as has the monetary policy accelerator. Now we are going downhill, the monetary accelerator is on, as is the financial accelerator, and there is no proper focus on financial stability. The US will have to decide which of the two pedals they use to slow down. If you reduce the fiscal accelerator, costs will rise in the future as the next round of fiscal policy will be based on physical infrastructure and then on human capital. The cash accelerator does not add anything to economic growth, only to the prices of financial assets. The right thing to do would be to slow down monetary policy, maintain the fiscal accelerator, and increase pressure on rules to ensure financial stability. If this continues, the monetary accelerator will have to abandon the financial accelerator, and this will be tragic for future years of growth.

General internet buff. Hardcore music maven. Typical foodaholic. Friendly student.
Politics
The dollar continues to reflect the political scenario

Yesterday, financial agents evaluated the opposite decision of the Federal Supreme Court (STF) regarding the so-called secret budget. In addition, a decision was made by STF Minister Gilmar Méndez to issue an injunction that would exclude the Bolsa Família from the spending cap rule, with investors trying to understand how this measure would affect the processing of the transitional PEC in the Chamber of Deputies. Oh this PEC!!!!
Since he is an exchange investor, any reading that the budget will be exceeded or become more flexible will negatively affect the exchange market, whether through the PEC or in any other way. We will continue with volatility today.
Looking beyond, the US Central Bank (Fed), although slowing down the pace of monetary tightening at its December meeting, issued a tougher-than-expected statement warning that its fight against inflation was not yet over, raising fears that rising US interest rates will push the world’s largest economy into recession.
The currency market continues to react to political news. The voting on the PEC is saved for today. It is expected that it will indeed be reviewed to open the way tomorrow for discussions on the 2023 budget.
For today on the calendar we will have an index of consumer confidence in the eurozone. Good luck and good luck in business!!

General internet buff. Hardcore music maven. Typical foodaholic. Friendly student.
Politics
Andrés Sánchez consults with the Ministry of Sports, but refuses a political post.

The former president of the Corinthians dreams of working for the CBF as a national team coordinator. He was consulted shortly after Lula’s election.
Former Corinthians president Andrés Sánchez was advised to take a position in the Ministry of Sports under the administration of Lula (PT). However, he ruled out a return to politics. dreams of taking over the coordination of CBF selectionHow do you know PURPOSE.
No formal invitation was made to the former Corinthian representative, only a consultation on a portfolio opportunity with the new federal government, which will be sworn in on January 1, 2023.
Andrés was the Federal MP for São Paulo from 2015 to 2019. At that time he was elected by the Workers’ Party. However, the football manager begs to stay in the sport, ruling out the possibility of getting involved in politics again.
Andrés Sanchez’s desire is to fill the position of CBF tackle coordinator, which should become vacant after the 2022 World Cup. Juninho Paulista fulfills this function in Brazil’s top football institution.
The former president of Corinthians was in Qatar to follow the World Cup along with other figures in Brazilian football. During his time in the country, he strengthened his ties with the top leadership of the CBF.
Editors’ Choice

General internet buff. Hardcore music maven. Typical foodaholic. Friendly student.
Politics
The EU has reached a political agreement on limiting gas prices – 19.12.2022

BRUSSELS, DECEMBER 19 (ANSA). European Union countries reached a political agreement on Monday (19) to impose a natural gas price ceiling of 180 euros per megawatt hour (MWh). The main sources of income for Russia and the minimization of the use of energy as a weapon by the regime of Vladimir Putin.
The agreement was approved by a supermajority at a ministerial meeting of member states in Brussels, Belgium, after months of discussions about the best way to contain the rise in natural gas prices in the bloc caused by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. .
The value set by the countries is well below the proposal made by the European Commission, the EU’s executive body, in November: 275 EUR/MWh. However, the countries leading the cap campaign were in favor of an even lower limit, around 100 EUR/MWh.
Germany, always wary of price controls, voted in favor of 180 euros, while Austria and the Netherlands, also skeptical of the cap, abstained. Hungary, the most pro-Russian country in the EU, voted against.
The instrument will enter into force on 15 February, but only if natural gas prices on the Amsterdam Stock Exchange exceed 180 euros/MWh for three consecutive days. In addition, the difference compared to a number of global benchmarks should be more than 35 euros.
Italy, the EU’s biggest supporter of the ceiling, has claimed responsibility for the measure. “This is a victory for Italy, which believed and worked for us to reach this agreement,” Environment and Energy Minister Gilberto Picetto tweeted.
“This is a victory for Italian and European citizens who demand energy security,” he added.
Currently, the gas price in Amsterdam is around 110 EUR/MWh, which is already a reflection of the agreement in Brussels – in August the figure even broke the barrier of 340 EUR/MWh.
However, Russia has already threatened to stop exports to countries that adhere to the ceiling. (ANSA).

General internet buff. Hardcore music maven. Typical foodaholic. Friendly student.
-
World4 years ago
The Gabby Petito case. Brian Landry set up camp with his family after his girlfriend disappeared
-
Top News6 years ago
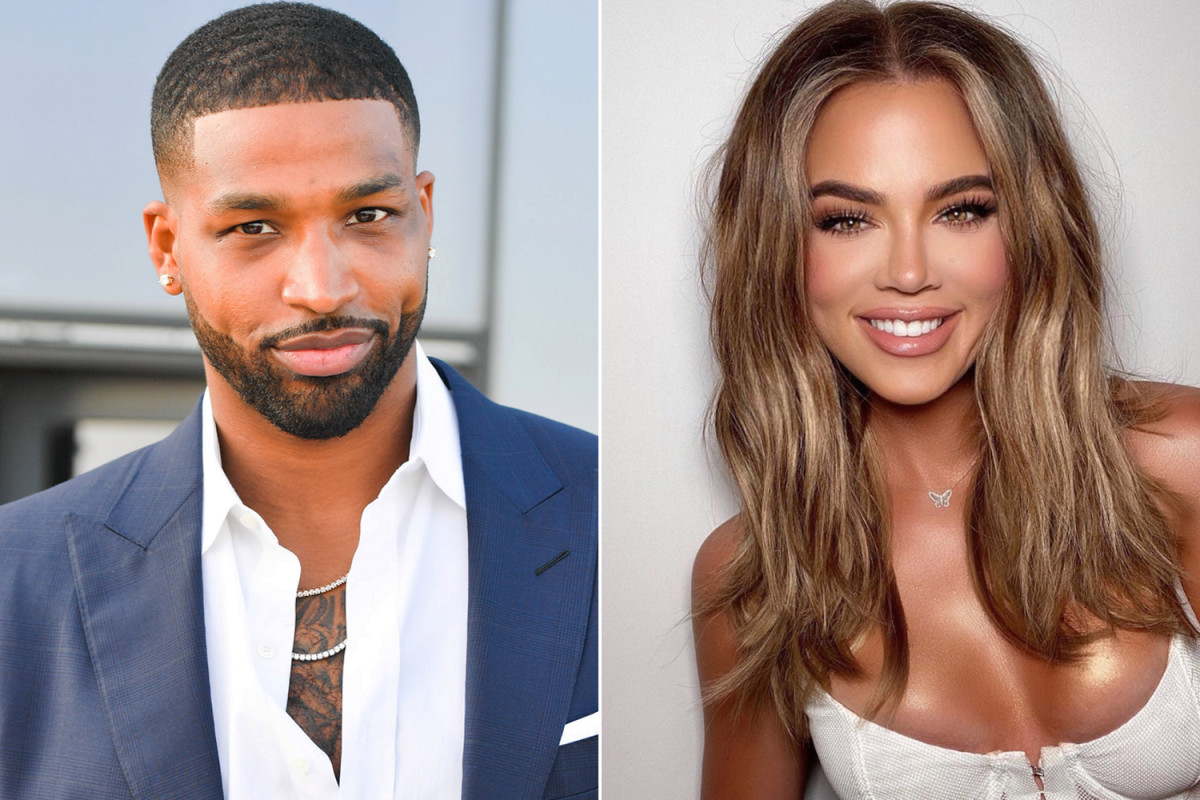
Tristan Thompson reacts to Khloé Kardashian’s new appearance
-
Economy3 years ago
Everything has been delivered. 10 Bugatti Centodieci are already in the hands of the owners
-
Top News6 years ago
TLC ‘sMothered’ recap: ‘Party curled up,’ boyfriend problem
-
Top News6 years ago
Alex Cooper hosts a solo podcast
-
Top News6 years ago
2021 Ford Bronco price: Here’s how much the 2-door and 4-door cost
-
Tech5 years ago
Fall Guys is supplying out a legendary costume and Kudos as an apology present
-
Top News6 years ago
Chiara de Blasio was ‘very cold’ during the arrest of the protest: witness